FAQs
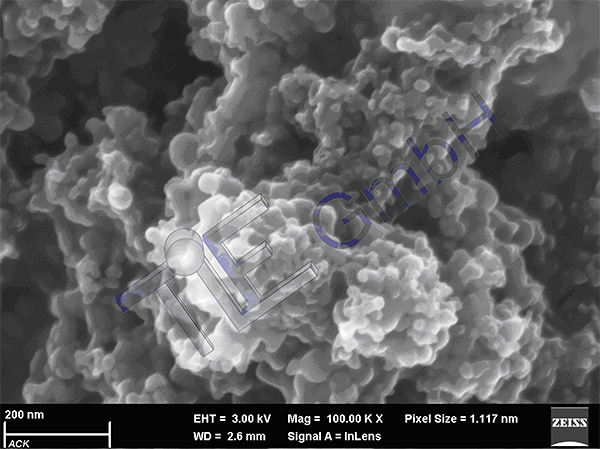
Carbon Nanohorns (CNH) are well characterised 5 to 150 nm long cone-shaped single-walled conical nanostructures of about 3 to 25 nm diameter. By adding CNH to different types of base materials specific properties of the materials can be modified (e.g. strength, abrasion, friction, electrical/thermal conductivity). Tests have been performed so far to determine the influence of CNH on the properties of CNT (bucky papers), on the properties of thermoplastic resins and fibres, of rubber, of lacquer, of light metals/light metals sinters and of ceramics.
CNH build, through spontaneous self-arrangement, aggregates up to some µm size. Contrary to carbon black, both the aggregates and the single particles are structured. CNH differ from the more commonly known fibrous and most often multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) by their three-dimensional structure, the higher purity (absence of metals / catalysts) and the possibility to disperse them without functionalization in water.
TIE GmbH, in cooperation with a number of research partners, is exploring further the application potential of CNH for industrial applications. Partners for further application testing are welcome. CNH are supplied by TIE GmbH in industrial quantities in different purities as dry powder material and suspended in water.
 |
 |
TIE GmbH supplies two types of CNH in powder form:
CNH Type A contains very fine grained CNH-Clusters (separation through cyclone). The carbon content is above 95 % wt. The CNH content is above 99 % wt. of carbon.
CNH Type B contains fine grained CNH-Clusters. The carbon content is above 95 % wt. The CNH content is above 99 % wt. of carbon.
CNH can be made available as suspension in non-polar solvents. These suspensions have the advantage that particles are suspended in the solvent and cannot be easily released to the atmosphere. On the other hand non-polar solvents often imply own safety requirements, as they can form flammable or explosive vapours. Furthermore, the relative (mass) CNH content is small (a few mass-percents at maximum).
Thus TIE and its partners have recently been developing a new type of CNH. The CNH of Type B are suspended in purified water without additional additives. The product is a water-based paste called "Type F" with a relative high content of CNH (about 8% wt. upwards).
Through further dewatering of Type F a CNH-paste can be produced with a content of up to 80 to 90 % wt. CNH (residual water content 10 to 20 %). This product is called "Type W" and has the consistency of a humidified powder.
With regard to health and safety both types have incontestable advantages. Types B and W provide for safe handling of CNH in laboratory or production units without formation of flammable or explosive vapours and without uncontrolled release of nanoparticles to the atmosphere.